In this tutorial you will learn how to use char_length() String function of mysql with java servlet
Mysql CHAR_LENGTH() Function Example Using Java Servlet
In this tutorial you will learn how to use char_length() String function of mysql with java servlet
CHAR_LENGTH() method of mysql, a string /character is passed into its parameter and then it gives back the number of characters by which the string is made including white spaces. CHARACTER_LENGTH() function is similar to the CHAR_LENGTH() function.
Syntax :
char_length('expression')
character_length('expression')
Here expression could be a string, a character, special character or numbers.
Now, since I have to use this function in java servlet program, therefore I have created a java servlet class named MysqlCharLengthServlet which extends the HttpServlet class. In the body of class I overridden the method doGet() and created an objects of HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse into its parameter. Inside the doGet() method first I set the mime type that in which format the browser will show the output. In the next line I used the getWriter() method of ServletResponse interface with the object of HttpServletResponse. HttpServletResponse interface extends this method from the ServletResponse. In Next step I am taking an input using the getParameter() method of ServletRequest with the object of HttpServletRequest. In continue we have to establish a connection between java code and database system. So, since I am using Mysql in the example given below therefore, I am loading the driver of mysql and make a connection by using the getConnection() method of DriverManager class. It returns a Connection. Further I am passing the query "SELECT CHAR_LENGTH("+"'"+chr+"'"+")"; (This query will return the length of string for the value input by the user. In this query chr is a variable name that stores the value that is given by the user. getParameter() method is used to take and store the value of this variable in source/java code.) into the parameter of prepareStatement() method of Connection interface which gives an object of PreparedStatement interface. In the next line I used the executeQuery() method of PreparedStatement interface which returns a ResultSet object that holds the result of query. At last I have extracted the result from the ResultSet object.
Example :
CharLength.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Length of Character or String</title> </head> <body> <form method="get" action="MysqlCharLengthServlet"> <table><tr><td>Enter a String or a Character <input type="text" name="txtName"/></td></tr> <tr><td align="center"><input type="submit" value="Find LengthOfString"/> </table> </form> </body> </html>
MysqlCharLengthServlet.java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class MysqlCharLengthServlet extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String chr = request.getParameter("txtName");
String className = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.13";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection con;
PreparedStatement ps;
ResultSet rs;
try
{
Class.forName(className);
con=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql = "SELECT CHAR_LENGTH("+"'"+chr+"'"+")";
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
sql = rs.getString(1);
out.println("Length of string "+"\""+chr+"\" = "+sql);
}
}
catch(SQLException sx)
{
out.println(sx);
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException cx)
{
out.println(cx);
}
}
}
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <display-name>mysqlStringFunction</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>MysqlCharLengthServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>MysqlCharLengthServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>MysqlCharLengthServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/MysqlCharLengthServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Output
When you will execute the above example you will get the output as :
1.
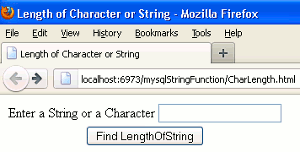
2. String entered without white space.

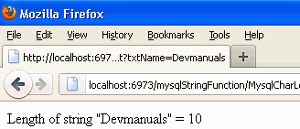
3. Output without white space.
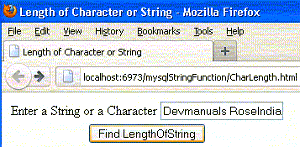
4. String entered with white space.
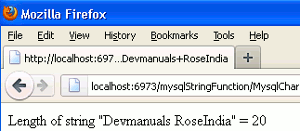
5. Output including white space.


[ 0 ] Comments