This section contains the detail about @Test annotation in JUnit.
@Test annotation in JUnit
The Test annotation tells JUnit that the public void method to which it is attached can be run as a test case. For example :
Pet.java
package devmanuals.junit;
public class Pet {
public Pet() {
}
public String bow() {
return "Bow";
}
}
PetTest.java(Test Class)
package devmanuals.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import devmanuals.junit.Pet;
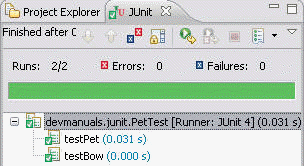
public class PetTest {
@Test
public void testPet() {
}
@Test
public void testBow() {
Pet testPet = new Pet();
assertTrue("Bow".equals(testPet.bow()));
}
}
Output
Optional Parameter of Test Annotation
The Test annotation supports two optional parameters. The first, expected, declares that a test method should throw an exception. If it doesn't throw an exception or if it throws a different exception than the one declared, the test fails. For example, the following test succeeds :
package devmanuals.junit;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.junit.Test;
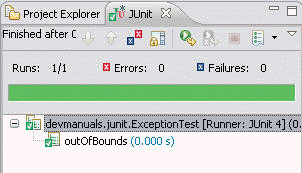
public class ExceptionTest {
@Test(expected = IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void outOfBounds() {
new ArrayList<Object>().get(1);
}
}
Output :
The second optional parameter, timeout, causes a test to fail if it takes longer than a specified amount of clock time (measured in milliseconds). The following test fails :
package devmanuals.junit;
import org.junit.Test;
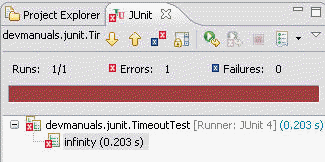
public class TimeoutTest {
@Test(timeout = 100)
public void infinity() {
while (true)
;
}
}
Output:
As expected above test fails :


[ 0 ] Comments