This section contains the detail about the Files and I/O in java.
Files and I/O
The every class which you need to perform input and output (I/O) is contained by java.io package.
A sequence of data can be defined as a stream. To read data from a source we used InputStream and to write data to destination, we need OutputStream.
Reading Console Input
Java input console is accomplished by reading from System.in. To obtain a character-based stream that is attached to the console, you wrap System.in in a BufferedReader object, to create a character stream. Here is most common syntax to obtain BufferedReader :
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
Once BufferedReader is obtained, we can use read( ) method to reach a character or readLine( ) method to read a string from the console.
Example of Reading Characters
import java.io.*;
class BRRead {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
char c;
// Create a BufferedReader using System.in
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter characters, 'q' to quit.");
// read characters
do {
c = (char) br.read();
System.out.println(c);
} while(c != 'q');
}
}
Output :
|
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>javac BRRead.java C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>java BRRead Enter characters, 'q' to quit. 123abcq 1 2 3 a b c q |
Example of Reading Strings
import java.io.*;
class BRReadLines {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
// Create a BufferedReader using System.in
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
System.out.println("Enter lines of text.");
System.out.println("Enter 'end' to quit.");
do {
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
} while(!str.equals("end"));
}
}
Output :
|
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>javac BRReadLines.java C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>java BRReadLines Enter lines of text. Enter 'end' to quit. This is line one This is line one This is line two This is line two end end |
Writing Console Output
Using print( ) and println( ), you can easily write to console.The
PrintStream class has definition of these method. These objects are referenced
by "System.out". Even though System.out is a byte stream, using it for simple
program output is still acceptable.
Because PrintStream is an output stream derived from OutputStream, it also
implements the low-level method write( ). Thus, write( ) can be used to write to
the console.
Example :
import java.io.*;
class WriteDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int b;
b = 'A';
System.out.write(b);
System.out.write('\n');
}
}
Output :
|
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>javac BRReadLines.java C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>java BRReadLines A |
Reading & Writing File
A sequence of data can be defined as stream. To read data from Source, we use InputStream. To write data to target we use OutputStream.
Here is a hierarchy of classes to deal with Input and Output streams :
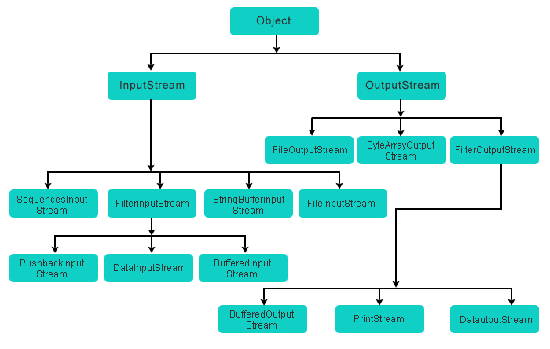
FileInputStream
FileInputStream is used to read data from the files. Objects can be created using the keyword new.
Following constructor takes a file name as a string to create an input stream object to read the file :
InputStream f = new FileInputStream("C:/java/hello");
But before this you need to create a file object using "File()" method as follows :
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
InputStream f = new FileInputStream(f);
FileOutputStream
For creating a file and writing data to it , we use FileoutputStream. Following constructor takes a file object to create an output stream object to write the file. First we create a file object using File() method as follows :
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(f);
Example :
The below code would create file test.txt and would write given numbers in binary format :
import java.io.*;
public class fileStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("C:/textfile1.txt");
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(f);
if (f.exists()) {
String str = "This data is written through the
program";
fop.write(str.getBytes());
fop.flush();
fop.close();
System.out.println("The data has been written");
}
else
System.out.println("This file is not exist");
try {
InputStream is = new
FileInputStream("C:/textfile1.txt");
int size = is.available();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print((char) is.read());
}
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print("Exception");
}
}
}
Output :
|
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>javac fileStreamDemo.java C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_18\bin>java fileStreamDemo The data has been written This data is written through the program |


[ 0 ] Comments